 COA COA |
 MSDS MSDS |
 HPLC HPLC |
 NMR NMR |
| CAS No: | 1232030-35-1 |
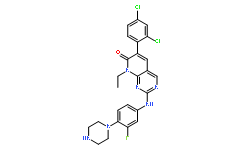
| Molecular formula(MF) | C25H23Cl2FN6O |
| Molecular Weight(MW): | 513.39 |
| Alias |
| In vitro | DMSO | 22 mg/mL (42.85 mM) |
|---|---|---|
| Water | <1 mg/mL | |
| Ethanol | <1 mg/mL | |
| In vivo |
| Description | FRAX486 is a potent p21-activated kinase (PAK) inhibitor with IC50 values of 14, 33, 39 and 575 nM for PAK1, PAK2, PAK3 and PAK4 respectively. | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Targets |
|
||||||||
| In vitro |
In WPMY-1 cells, FRAX486 induces concentration-dependent (1-10 μM) degeneration of actin filaments. This was paralleled by attenuation of proliferation rate, being observed from 1 to 10 μM FRAX486. Cytotoxicity of FRAX486 in WPMY-1 cells is time- and concentration-dependent. In WPMY-1 cells, effects of FRAX486 on actin organization, survival, and proliferation occurred already at concentrations of 1-5 μM. In these concentrations, full inhibition of PAK1-3 may be expected, while PAK4 may be inhibited only partially[2]. |
||||||||
| In vivo | FRAX486 crosses the blood-brain barrier and that therapeutically useful concentrations of FRAX486 are in the brain as early as 1 h and remain as long as 24 h after administration, with the maximum concentration in the target tissue at 8 h. Daily dosing results in steady-state levels of FRAX486 in the brain. FRAX486 specifically rescues the Fmr1 KO abnormality in which the spine phenotype is present in apical neurons and not simply decreasing spine density irrespective of genotype or existence of a phenotype. Also, FRAX486 reduces hyperactivity and stereotypical movements, both of which are phenotypes that characterize the mouse model of Fragile X syndrome[3]. |